The production of artificial snow to cover skiing slopes is of major importance for the planning certainty in winter tourism. Due to innovations in energy efficiency but also because of the progressing global warming an increasing significance of technical snowmaking is assumable for the future. In this context, alpine reservoir ponds are of crucial relevance and will probably increase in number. However, to guarantee optimal security in consideration of potential hazards like landslides, a systematical or continuous monitoring of new and existing pond locations is essential.
Currently, reservoir ponds are surveyed with ground-based methods like total stations, GPS or laser scanning. Unfortunately, these technologies bring along some severe disadvantages. Especially to mention is the point-like character of the measurements and extensive measurement intervals, which are sometimes incomplete, too. Thus, potential threats might be noticed late or, in worst cases, not at all. For the identification of new hazard areas and the planning of new sites, there are currently no area-wide ground movement maps (based on historical data) that would significantly simplify the search for safe sites.
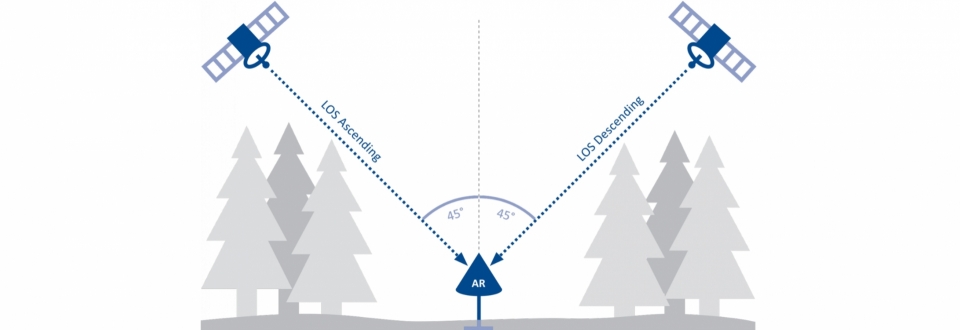
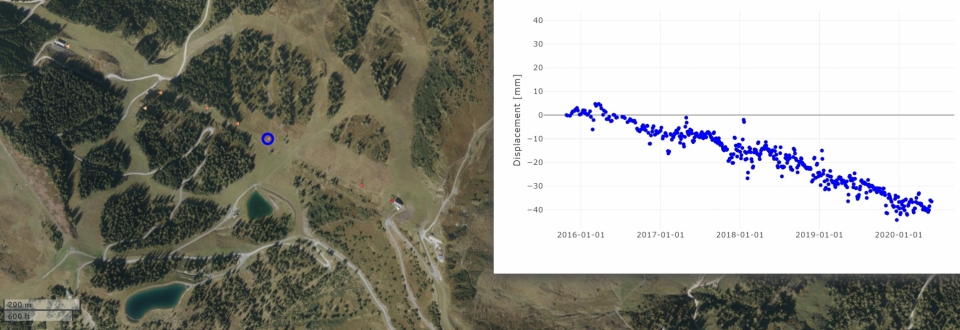
Satellite-based Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR), which has been used in a pilot study for the monitoring of reservoir ponds just once, has the potential to fill these gaps. Thanks to satellite-based InSAR, ground movements can be measured directly, area-wide and precisely within the accuracy of millimeters. SB-InSAR is a proven technology, the first ERS-1 radar satellite was commissioned by the European Space Agency (ESA) back in 1992. Limiting factors then included the low resolution (30 * 30 m) and the long return time of 35 days (reattainment of the starting point). When the German Earth observation satellite TerraSAR-X was put into operation in 2008 it already achieved a resolution of 1 * 1 m and a return period of 11 days. This made it particularly suitable for engineering issues.
The project RESERVOIR aims primarily to analyze the applicability of satellite-based InSAR data for an innovative management of alpine reservoir ponds at selected locations. Doing so, satellite-based InSAR should be utilized as key technology by the current level of knowledge. As part of an initial feasibility study, RESERVOIR is systematically exploring the application of SB-InSAR data in reservoir management for the first time, thereby making a significant contribution to improving long-term planning and infrastructure security.